Find producer and consumer surpluses if the supply curve is given by  , and the demand curve is given by
, and the demand curve is given by  .
.
| Foundations:
|
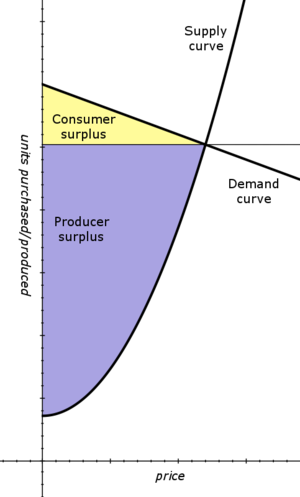
| The supply curve and the demand curve are tied to price of a product. As the price goes up, manufacturers would be willing to produce more, so the supply curve is usually increasing. On the other hand, as the price goes up, fewer consumers might purchase the product, so the demand curve is usually decreasing.
At some sale price, these two curves intersect at an equilibrium point. When we speak of consumer surplus and producer surplus, we are talking about the total area under between the horizontal line through the equilibrium level of units, and the demand curve or supply curve, respectively. We need to integrate the areas indicated on the graph to find actual values for these two surpluses.
|
Solution:
| Step 1:
|
Find the equilibrium point: Since we are given equations for both curves, we need to set them equal and solve for  . Setting them equal, we have . Setting them equal, we have
|

|
| If we move everything to one side and factor, we find
|

|
This has only one positive root,  . at this point we have the associated height . at this point we have the associated height 
|
| Step 2:
|
Consumer Surplus: We need to find the triangular area in the graph, and this will mean integrating between  and equilibrium and equilibrium  -value, -value,  . Also, we will integrate from the horizontal line through the equilibrium, . Also, we will integrate from the horizontal line through the equilibrium,  , up to the demand curve, , up to the demand curve,  . We have . We have
|

|
| Step 3:
|
| Producer Surplus: Now, we wish to integrate the area from the supply curve up to the horizontal line through our equilibrium point. We have
|

|
| Final Answer:
|
The consumer surplus is  , while the producer surplus is , while the producer surplus is  . .
|
Return to Sample Exam