Prototype Calculus Question
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
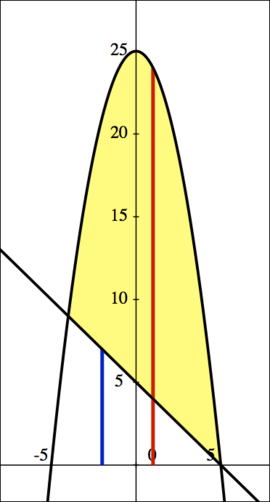
Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating the area enclosed by and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=25-x^2 }
around the x-axis.
| Foundations |
|---|
| • Choose either shell or washer method. |
| • Find the appropriate radii. |
| • Determine the bounds of integration by finding when both functions have the same y value. |
| • Using the determined values, set up and solve the integral. |
Solution:
| Step 1: |
|---|
| Since we are rotating around the x-axis, the washer method would utilize tall rectangles with dx as their width. This seems like a reasonable choice, as these rectangles would be trapped between our two functions, allowing us to solve a single integral. |
| Step 2: |
|---|
| Since our rectangles will be trapped between the two functions, and will be rotated around the x-axis (where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=0 } ), we find |
| the inner radius is Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r = 5-x } , represented by the blue line, while |
| the outer radius is Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R = 25-x^2 } , represented by the red line. |
| Step 3: |
|---|
| We must set the two functions equal, and solve. More to follow... |