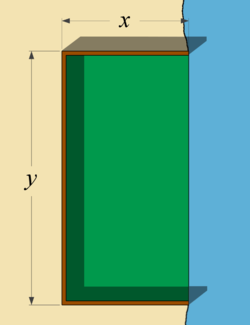
A dairy farmer plans to enclose a rectangular pasture adjacent to a river. To provide enough grass for his cows, the fenced pasture must contain 200 square meters of grass. If no fencing is required along the river, what dimensions will use the smallest amount of fencing?
| Foundations:
|
| As a word problem, we must begin by assigning variables in order to construct useful equation(s). As an optimization problem, we will be taking a derivative of one of our equations in order to find an extreme point.
|
Solution:
| Step 1:
|
Declare Variables: We are attempting to enclose a rectangular area, such that we use as little fencing as possible for the three fenced sides. Let's use Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x}
and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y}
as indicated in the image, and simply call the length of fencing required  . .
|
| Step 2:
|
| Form the Equations: With the variables declared, we need two fences of length Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x}
and one fence of length Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y}
. Together, we need a total length of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle L=2x+y}
.
|
| On the other hand, we know that the pasture has a fixed area of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 200}
square meters. Thus, we also know that Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle xy=200}
.
|
| Step 3:
|
| Optimize: Since Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle xy=500}
, we also know Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=500/x}
. Plugging this into our equation for length, we have
|
| Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle L(x) = 8x + 5\cdot \frac{500}{x} = 8x + \frac{2500}{x}.}
|
| We now take the derivative to find
|
| Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle L'(x)=8-\frac{2500}{x^2}= \frac{8x^2-2500}{x^2}.}
|
| The denominator can never be zero, and if we set the numerator to zero we find
|
| Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=\pm\sqrt{\frac{2500}{8}} = \pm\frac{50}{2\sqrt{2}} =\pm\frac{\,\,25}{\sqrt{2}}.}
|
| Of course, we can't have negative fencing lengths, so we can ignore the negative root. Finally, we use the area relation to find
|
| Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y =\frac{500}{25\sqrt{2}} = \frac{500\sqrt{2}}{25} = 20\sqrt{2}. }
|
| Thus, the least amount of fencing is used when we size our Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 500}
sq. ft. pens as Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 20\sqrt{2}}
feet by Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 25/\sqrt{2}}
feet.
|
Return to Sample Exam