Consider the region bounded by the following two functions:
-
 and
and 
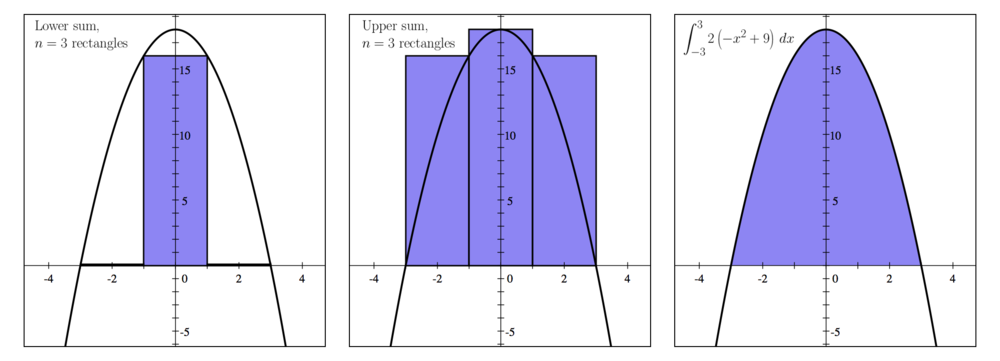
- a) Using the lower sum with three rectangles having equal width, approximate the area.
- b) Using the upper sum with three rectangles having equal width, approximate the area.
- c) Find the actual area of the region.
| Foundations:
|
| Recall:
|
- 1. The height of each rectangle in the lower Riemann sum is given by choosing the minimum
|
 value of the left and right endpoints of the rectangle. value of the left and right endpoints of the rectangle.
|
- 2. The height of each rectangle in the upper Riemann sum is given by choosing the maximum
|
 value of the left and right endpoints of the rectangle. value of the left and right endpoints of the rectangle.
|
- 3. The area of the region is given by
 for appropriate values for appropriate values 
|
Solution:
(a)
| Step 1:
|
| We need to set these two equations equal in order to find the intersection points of these functions.
|
| So, we let
|

|
Solving for  we get we get 
|
This means that we need to calculate the Riemann sums over the interval ![{\displaystyle [-3,3].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f2fd4965b1b60b2cd619e047375423a5fbe2d03a)
|
| Step 2:
|
Since the length of our interval is  and we are using and we are using  rectangles, rectangles,
|
each rectangle will have width 
|
| Thus, the lower Riemann sum is
|

|
(b)
| Step 1:
|
As in Part (a), the length of our inteval is  and and
|
| each rectangle will have width Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2.}
(See Step 1 and 2 for (a))
|
| Step 2:
|
| Thus, the upper Riemann sum is
|
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2(f(-1)+f(-1)+f(1))\,=\,2(16+16+16)\,=\,96.}
|
(c)
| Step 1:
|
| To find the actual area of the region, we need to calculate
|
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \int_{-3}^3 2(-x^2+9)~dx.}
|
| Step 2:
|
| We integrate to get
|
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{array}{rcl} \displaystyle{\int_{-3}^3 2(-x^2+9)~dx} & = & \displaystyle{2\bigg(\frac{-x^3}{3}+9x\bigg)\bigg|_{-3}^3}\\ &&\\ & = & \displaystyle{2\bigg(\frac{-3^3}{3}+9\times 3\bigg)-2\bigg(\frac{-(-3)^3}{3}+9(-3)\bigg)}\\ &&\\ & = & \displaystyle{2(-9+27)-2(9-27)}\\ &&\\ & = & \displaystyle{2(18)-2(-18)}\\ &&\\ & = & \displaystyle{72}.\\ \end{array}}
|
| Final Answer:
|
| (a) Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 32}
|
| (b) Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 96}
|
| (c) Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 72}
|
Return to Sample Exam








![{\displaystyle [-3,3].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f2fd4965b1b60b2cd619e047375423a5fbe2d03a)