Difference between revisions of "009B Sample Final 1, Problem 3"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
::::::<math>y=\sin x</math> and <math style="vertical-align: -13px">y=\frac{2}{\pi}x.</math> | ::::::<math>y=\sin x</math> and <math style="vertical-align: -13px">y=\frac{2}{\pi}x.</math> | ||
| − | <span class="exam">a) Find the three intersection points of the two given functions. (Drawing may be helpful.) | + | ::<span class="exam">a) Find the three intersection points of the two given functions. (Drawing may be helpful.) |
| − | <span class="exam">b) Find the area bounded by the two functions. | + | ::<span class="exam">b) Find the area bounded by the two functions. |
{| class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style = "text-align:left;" | {| class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style = "text-align:left;" | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
|Recall: | |Recall: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |'''1.''' You can find the intersection points of two functions, say <math style="vertical-align: -5px">f(x),g(x),</math> | + | | |
| + | ::'''1.''' You can find the intersection points of two functions, say <math style="vertical-align: -5px">f(x),g(x),</math> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | ::by setting <math style="vertical-align: -5px">f(x)=g(x)</math> and solving for <math style="vertical-align: 0px">x</math> | + | :::by setting <math style="vertical-align: -5px">f(x)=g(x)</math> and solving for <math style="vertical-align: 0px">x.</math> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |'''2.''' The area between two functions, <math style="vertical-align: -5px">f(x)</math> and <math style="vertical-align: -5px">g(x)</math> | + | | |
| + | ::'''2.''' The area between two functions, <math style="vertical-align: -5px">f(x)</math> and <math style="vertical-align: -5px">g(x),</math> is given by <math>\int_a^b f(x)-g(x)~dx</math> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | ::for <math style="vertical-align: -3px">a\leq x\leq b</math> | + | :::for <math style="vertical-align: -3px">a\leq x\leq b,</math> where <math style="vertical-align: -5px">f(x)</math> is the upper function and <math style="vertical-align: -5px">g(x)</math> is the lower function. |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 37: | Line 39: | ||
!Step 2: | !Step 2: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Setting <math style="vertical-align: -14px">\sin x=\frac{2}{\pi}x</math> | + | |Setting <math style="vertical-align: -14px">\sin x=\frac{2}{\pi}x,</math> we get three solutions: |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | ::<math>x=0,\frac{\pi}{2},\frac{-\pi}{2}.</math> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |So, the three intersection points are <math style="vertical-align: -15px">(0,0),\bigg(\frac{\pi}{2},1\bigg),\bigg(\frac{-\pi}{2},-1\bigg)</math> | + | |So, the three intersection points are <math style="vertical-align: -15px">(0,0),\bigg(\frac{\pi}{2},1\bigg),\bigg(\frac{-\pi}{2},-1\bigg).</math> |
|- | |- | ||
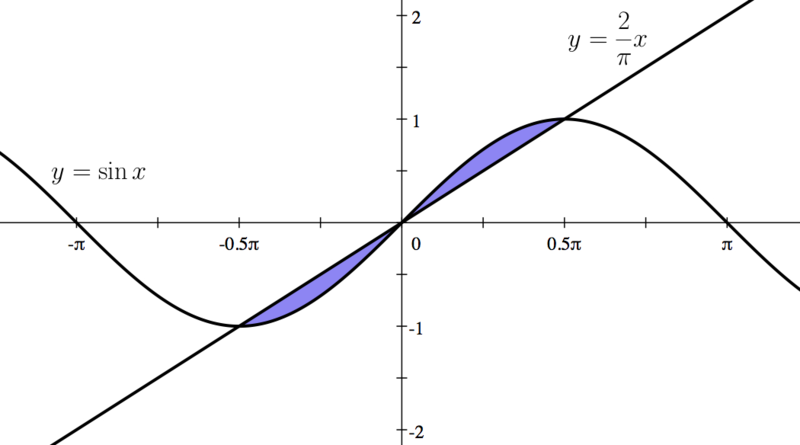
|You can see these intersection points on the graph shown in Step 1. | |You can see these intersection points on the graph shown in Step 1. | ||
Revision as of 11:54, 18 April 2016
Consider the area bounded by the following two functions:
- and
- a) Find the three intersection points of the two given functions. (Drawing may be helpful.)
- b) Find the area bounded by the two functions.
| Foundations: |
|---|
| Recall: |
|
|
|
|
Solution:
(a)
| Step 1: |
|---|
| First, we graph these two functions. |
| Step 2: |
|---|
| Setting Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sin x=\frac{2}{\pi}x,} we get three solutions: |
|
| So, the three intersection points are Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (0,0),\bigg(\frac{\pi}{2},1\bigg),\bigg(\frac{-\pi}{2},-1\bigg).} |
| You can see these intersection points on the graph shown in Step 1. |
(b)
| Step 1: |
|---|
| Using symmetry of the graph, the area bounded by the two functions is given by |
|
| Step 2: |
|---|
| Lastly, we integrate to get |
|
| Final Answer: |
|---|
| (a) Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (0,0),\bigg(\frac{\pi}{2},1\bigg),\bigg(\frac{-\pi}{2},-1\bigg)} |
| (b) Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\frac{\pi}{2}+2} |